Robotic Process Automation & Insurance Industry | Pyramid Solutions
Insurance Companies can save 30% to 50% of operational costs using RPA!
Most insurance companies such as life, health, property, car or travel insurance are overwhelmed with back-office processes. These companies often service large volumes of repetitive business practices that prevent them from offering timely customer service, meeting growth and profit targets, and maintaining a strategic competitive advantage in the insurance market.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software and algorithms to simulate human actions in existing systems and applications. The software sits at the user interface level of an application and transmits data between systems, much in the same way that a human user would. There are no actual “robots” involved in the physical sense of the word; rather, the term is used because RPA software mimics human behavior, utilizing the same user interface a person would (through screen scraping or some other method) rather than Web services or APIs.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is at the peak of inflated expectation cycle, says Gartner. They estimate by 2022, 85% of large and very large organizations would have deployed some form of RPA solutions to automate their business. Overall, the global Robotic Process Automation software spend is expected to reach $2.4 billion in 2022.
RPA helps insurance companies streamline their processes and enhance their ability to increase the client base with Service Satisfaction. Many insurance companies – whether providers of health insurance, car insurance, property insurance, or travel insurance are heavily inundated with back-office processes. Insurers regularly handle claims-processing and underwriting as well as providing policy quotes. This means they are often overwhelmed with high volumes of repetitive business practices that prevent them from delivering timely customer service, meeting growth and profit expectations, and maintaining a competitive advantage in the insurance market.
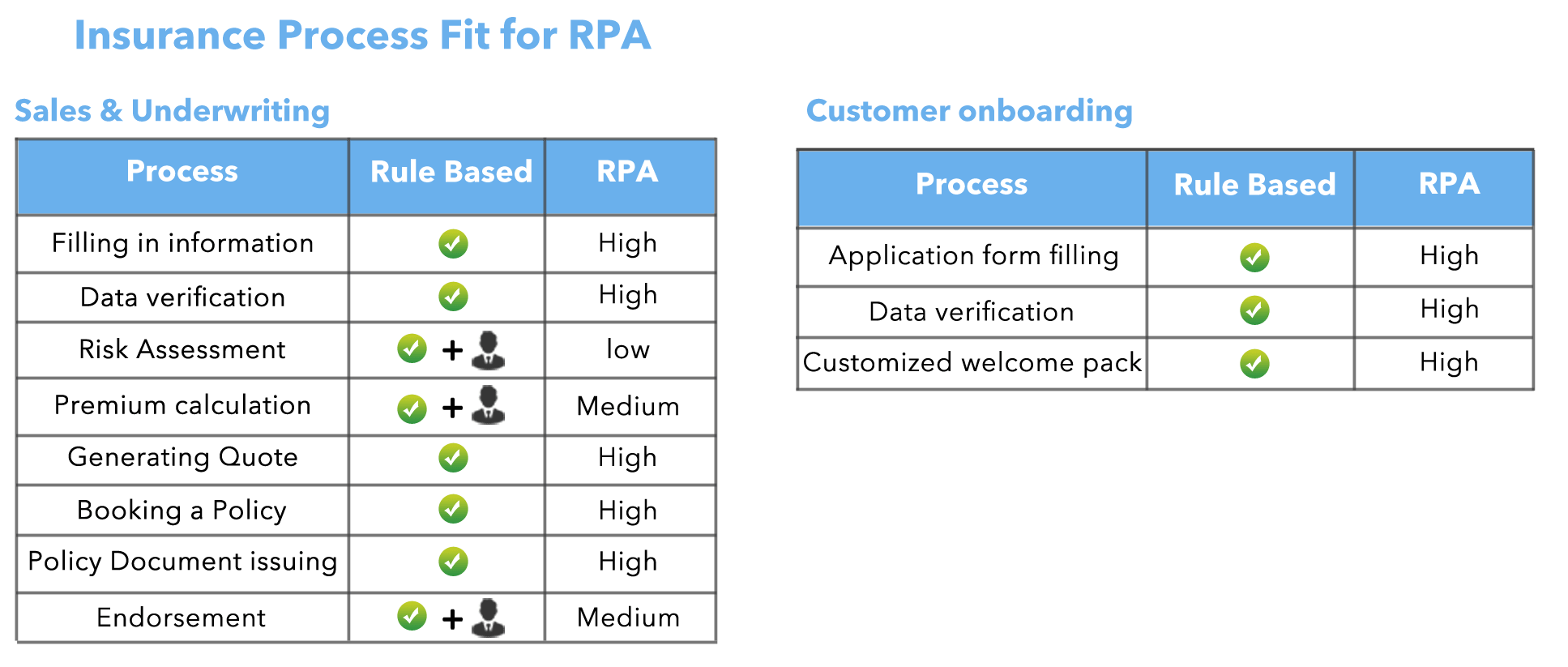
10 Use Cases for RPA in the Insurance Industry
- New Business & Underwriting
- Claims Processing
- Business and Process Analytics
- Manual Data Entry Process
- Usage of Legacy Applications
- Regulatory Compliance
- Scalability
- Blend New Technologies with Existing Systems
- Policy Cancellation
- Form Registration
RPA & Insurance Industry
RPA is able to capture manual steps that employees take to log into the software, search documents, and enter data and replicate them. Enterprise insurance firms can thus deploy a “digital workforce” for use-cases in claims processing, underwriting, and more.
RPA in Claims Processing
In general, RPA software is good for copying data from one source into another so long as that data appears the same in both sources every time. Claims adjusters are often tasked with collecting relevant information from claimants, hospitals, the police, and other insurers in order to make a decision on whether to pay out a claim and for how much.
Once the necessary records are obtained, the relevant data within them need to be translated to the insurer’s digital record of the incident. Without automation, claims adjusters would read through all of the records they collected and manually enter the necessary information into the system. In specific cases, RPA can help in this effort.
For example, someone might file an auto insurance claim immediately after their accident while they’re still on the road. In this case, they may need someone to tow their car. Some auto insurance customers pay for roadside assistance.
Traditionally, employees would need to manually input data from a claim about the customer’s accident into the system of a third-party mechanic that has an agreement with the insurance company. RPA software could automate the translation of this data between systems, thus speeding up the time it takes for a tow truck to reach the customer.
RPA in Underwriting
RPA has similar applications in underwriting, namely its ability to pool information from disparate sources into a single place. Underwriters need to evaluate the risk that potential customers, their homes, and their cars pose to the insurance carrier. The information they need to do this varies depending on what they need to assess.
Underwriters at larger auto insurers can check if a driver has been previously insured with similarly-sized auto insurers within a shared database. RPA software could do this instead, copying the name of the customer’s insurance carrier into the appropriate spot in the auto insurer’s CRM.
RPA software could translate data from public databases into the auto insurer’s CRM, allowing the underwriter to make a decision about whether or not they can offer the applicant a policy or not faster.
RPA in the long-term
Especially within industries, like insurance, which is highly dependent on the efficiency of their back office, RPA is being adopted at increasing rates in order to use to automate burdensome, high volume, and time-consuming business activities. This automation technology is being used to fight some of the biggest challenges faced by insurance providers, in order to promote long-term success opportunities and a competitive marketplace.
RPA can help insurers cut operations costs, achieve increased profits, make companies more competitive, increase growth, improve compliance, and provide faster customer service than ever possible before. Because of the flexibility and improvements that RPA can deliver, its adoption by insurance companies is only expected to become more global and inevitable. Rather than remaining just a technology option to choose from, RPA will eventually become a necessary component for insurance providers to remain competitive industry leaders.
Top RPA tools
UiPath
More than 2,750 enterprise customers and government agencies use UiPath’s Enterprise RPA platform to rapidly deploy software robots that perfectly emulate and execute repetitive processes, boosting business productivity, ensuring compliance and enhancing customer experience across back-office and front-office operations. UiPath is used by thousands of companies particularly in document management, contact center, insurance, healthcare, finance and accounting, human resources, and supply chains and to address major technical challenges, including data extraction and migration, process automation, application integration, and business process outsourcing.
Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere is a global leader in Robotic Process Automation (RPA), empowering customers to automate end-to-end business processes with software bots – digital workers that perform repetitive and manual tasks, resulting in dramatic productivity gains, improved customer experience and more engaged employees. The company offers the world’s only web-based and cloud-native intelligent automation platform combining RPA, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and analytics right out of the box, to help organizations rapidly start and scale their process automation journey. Automation Anywhere has deployed over 1.7 million bots to support some of the world’s largest enterprises across all industries.
Blue Prism
Blue Prism Group is a multinational software organization based in the UK. They pioneered RPA to reduce the high risk and low return processing work and data entry job manually. The technology used is based on Microsoft.net framework and it supports any type of platform and applications. It allows the design automation process that too within IT governance. The tool supports the internal and external decryption and encryption keys. The users are provided with audit logs enabling. The customized code of .NET provides a high rate of robustness.
Kofax Kapow
Kofax Inc. is a process automation software provider based in Irvine, California. They offer process management, RPA, e-signature, mobility and customer communication services to multiple customers in 70 countries worldwide. Kofax Kapow is the most efficient way to acquire, enhance and deliver information from any application and data source or enterprise system without coding. It supports all types of application environments and data sources, including websites, portals, enterprise systems, and legacy applications, Excel, Email, XML, JSON, CSV, and SQL. It can automatically publish robots with standard Java, .NET, SOAP, RESTful interface which is used to control robotic processes from external applications and remote systems.
RPA Tools Comparison:
| S.No | Parameters | Automation Anywhere | Blue Prism | UiPath |
| 1 | Accuracy | Rational | Set for BPO optimization | Set for Web Automation |
| 2 | Architecture | Client-Server | Client-Server | Orchestrator |
| 3 | Cognitive Capability | Very High | High | High |
| 4 | Learning | Basic knowledge of programming required | Ability to develop and control | Visual Designer |
| 5 | Macro-Recorder | Present | Absent | Present |
| 6 | Price | High | Medium | High |
| 7 | Trial Version availability | Available | No | Free edition available |
| 8 | Scalability | Limited | High-speed execution | Medium speed execution |
| 9 | Re-Usability | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 10 | Robots | Front & Back office | Front & Back office | Only Back office |
| 11 | Recorders | Yes | No | Yes |
| 12 | Access | App-based | App-based | Mobile Browsing |
| 13 | Process Designer | Script-based | Visual Process-based | Visual Process-based |
| 14 | Base Technology | Microsoft | C# | Microsoft |
| 15 | Reliability | High | Very high | Moderate |
Author Bio

Ketan Vegad
I have been associated with PCI for the last five and half years. I am ALMI, ACS and CSM certified professional with 12+ years of experience as Managing Consultant and Software Testing Professional with rich experience in Life/Annuity Insurance, General Insurance, Property & Casualty Insurance Domain.

